I think what you're looking for can be described as a graph where the graph edges are the sequence of connections from successive parents and children. The code below uses the igraph package to get the desired result.
library(igraph)
library(tidyverse)
df <- data.frame(pid = c(1,2,3,5),
cid = c(3,4,5,6))
wanted_df <- data.frame(pid = c(1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 5),
cid = c(3, 5, 6, 4, 5, 6, 6))
df_g = graph_from_data_frame(df, directed=TRUE)
wanted_df2 = map(V(df_g), ~ names(subcomponent(df_g, .x, mode="out"))) %>%
# Convert the list output to a data frame
map_df(~data.frame(cid=.x), .id="pid") %>%
# Get rid of rows where `pid` and `cid` are equal
filter(pid != cid) %>%
# Convert columns (from character) to numeric. Not necessary, but this makes the columns the same mode as the columns in `wanted_df`.
mutate(pid=as.numeric(pid),
cid=as.numeric(cid))
wanted_df2
#> pid cid
#> 1 1 3
#> 2 1 5
#> 3 1 6
#> 4 2 4
#> 5 3 5
#> 6 3 6
#> 7 5 6
identical(wanted_df, wanted_df2)
#> [1] TRUE
Created on 2019-02-24 by the reprex package (v0.2.1)
I haven't spent much time with the igraph package so I suspect my code is clunkier than it needs to be, but here's the general idea:
-
Convert
dfto a graph:graph_from_data_frame(df, directed=TRUE). -
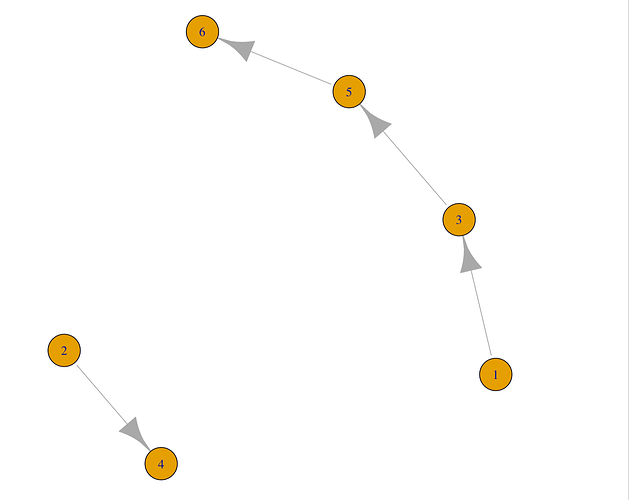
For a given vertex, get all vertices that can be reached from that vertex. We can see the graph we just created with
plot(df_g).Note that the plot shows visually that we can reach vertices 3, 5, and 6 from vertex 1; we can reach vertices 5 and 6 from vertex 3; etc. These are the relationships we wanted to capture by encoding your data as a graph.
To get all vertices that can be reached from a given vertex, we use the
subcomponentfunction. Here is the result from runningsubcomponentfor vertex 1:subcomponent(df_g, 1, mode="out") + 4/6 vertices, named, from 9c56ae3: [1] 1 3 5 6Note that this returns
c(1,3,5,6), which is what we wanted. You can reach vertices 3, 5, and 6 from vertex 1 (and you can also of course reach vertex 1 from vertex 1). -
Now we need to run the
subcomponentfunction on every vertex in the graphdf_g. We do that with themapfunction:map(V(df_g), ~ names(subcomponent(df_g, .x, mode="out"))).This returns a list containing the output of
subcomponentfor each vertex. The rest of the code is just to extract and reshape the output into a data frame.igraphfunctions seem to return complex objects whose structure and behavior I don't really understand, which is why I expect my code can be simplified with a little moreigraphknowledge.